
 |
CPSC 110-08: Computing on Mobile Phones
|
This set of questions is about number conversions. You might
want to look back
at this
homework
and this
lecture. You might also want to practice on these Khan
exercises:
Instructions: The next two problems ask you to read Pseudocode or App Inventor algorithm. Trace through each of them by hand, keeping track of the variables, to determine the answer to the questions.
Initially Var is 100 and N is 3. Var is then set to 97 (Var-N). The if statement tests whether Var is less than 97 (< 97). It is not so Var is set to 1.Set Var to 100 Set N to 3 Set Var to Var - N If Var < 97 then do: Set Var to 0 else-do: Set Var to 1
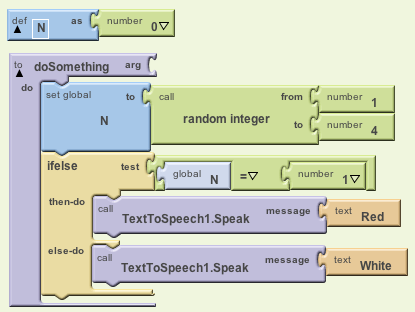
If this procedure is called 100 times, it would "speak" Red approximately
1/4 of the time, so around 25 times. It generates a random number between 1 and 4
inclusive so you would expect 1 to come up about 25 per cent of the time.
Instructions: The next problem asks you to write a Pseudocode
algorithm. Model your answers after the Pseudocode algorithm in question 5.
if N = M then do: Set global Var to 1 else do: Set global Var to 0